Unprecedented Opportunities Linked to The Internet in Africa
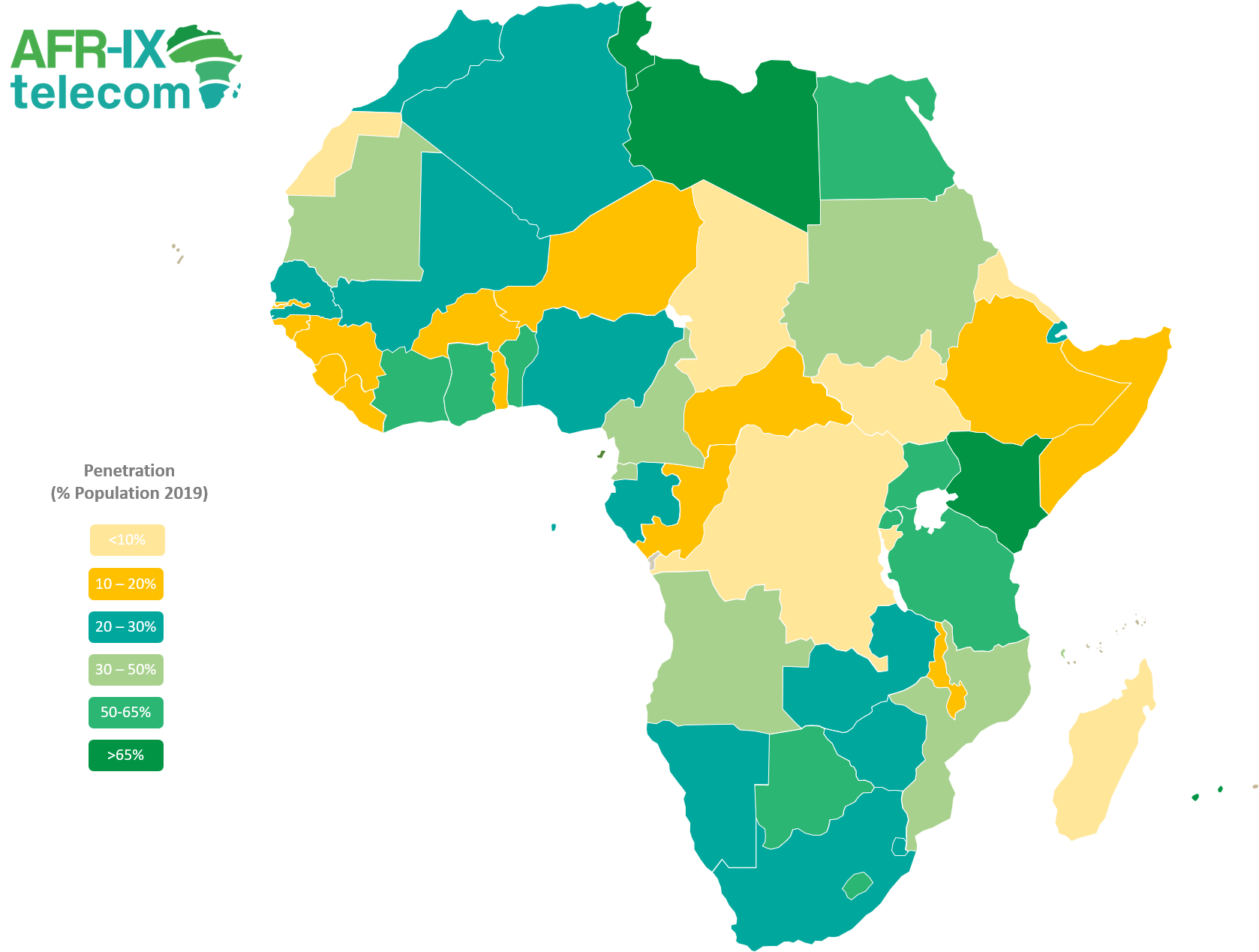
While mobile technology has evolved rapidly in Africa, achieving internet access to the continent still leaves a myriad of opportunities. How the internet will change Africa? According to Internet World Statistics, Africa only saw internet penetration of 39.3% at the end of March 2020, compared to 62.9% of internet users across the rest of the world. Digital services can easily be taken for granted by those who already have access to it but when we look at how life-altering it can be in terms of getting people closer to essential services, there are bountiful opportunities to increase the internet penetration to the populous continent.
A brief look at the internet’s progression in Africa
Africa first needed to make changes in policies and regulations to enable a susceptible environment for internet development. While there has been progress since the mid-1990s and the 2000s, the frontier for broadening access to the internet in Africa is undeniably happening now. Africa used to connect to the rest of the world through satellite connections until 2009, which were costly and not capable of mass capacity. In 2010, however, the Eastern Africa Submarine Cable System (EASSy) was installed undersea to connect East Africa to the rest of the world with fibre cables. Today, there are at least 37 African countries with one submarine cable landing
The demand for internet in Africa
Technology is crucial to advancing socioeconomic circumstances, as it means access to services such as online banking and shopping, education, healthcare, and e-agri services where information is exchanged for sustainable agriculture and rural development. The socio-economic reality of Africans can be best described by looking at recent figures cited by the World Bank, mentioning that approximately 640 million people live without electricity in Africa, while 416 million still live in poverty. This alone shows that there is vast room and demand for technological development.
Potential for expansive growth
[12:18] Moad Abufaress MahfoudBy 2016, Africa had 420 million mobile subscribers. Mobile broadband connections were expected to double to 500 million by 2020.
Mobile connectivity drives innovation, research, and education globally. It narrows the gap between Africa and the world.
Rapid development attracts mobile operators wanting to expand coverage in rural areas. This expansion creates a need for technicians to build the infrastructure.
Africans have shown enthusiasm for new digital technologies.
For example, Kenya’s Safaricom launched the M-Pesa mobile payment app in 2007. It allowed anyone in Kenya to send and receive money via SMS, even without a bank account.
Now, M-Pesa has 24.5 million users. Nearly 50% of Kenya’s population has adopted the technology.
What technology means for Africa
An increase in Africa’s internet penetration will translate into economic growth and the establishment of new commerce markets. Large corporations and governments have already recognised this potential in expanding Africa’s digital economy and their investments towards developing infrastructure bears witness to the opportunity it holds for the continent.
Investors in Africa’s digital expansion know that the demand is there. There will, in all likelihood, be an unprecedented growth in the digital space once Africa’s access to the internet closer resonates that of the rest of the world and the continent becomes a team player on a level playing field.
If you need a reliable network partner in Africa to discuss broadening access to the internet, contact AFR-IX telecom today.